Augmented reality refers to enhancing the visual rendering of an object on screen so that it may encompass some other objects as well, which may not be part of the environment but to a user, it seems as if the later are also within the picture. It uses methods of superimposing computer generated graphics, images or videos directly on the physical object while they are being viewed by a user on screen.
Basically, the virtual objects is combine together in a real environment. Typically, the visual,audio and graphical content made by computer are overlaid on into the users’ vision to provide extra information about their surroundings, or to provide visual guidance for the completion of a task. [1].
Augmented Reality is often defined using various methods. One of them, defined by [2] states that the systems should have the following three features in order to classified as having AR:
- it must have a tendency to merge together virtual and real environment.
- it must be capable enough of rendering its display in a real time and should provide interactive features to the user.
- it may have a 3-D representation of what it depicts.
Augmented Reality runs slightly parallel with Virtual reality, having obvious differences to it. In Virtual Reality, the user is fully immersed into the new environment, experiencing himself/herself to be part of the virtual environment but in augmented reality, the user experiences some enhanced visual depiction into the natural world and gets visual, sound and even touch feeling attained by living in their own natural world only. Another major difference between both of them is that in order to experience Virtual Reality, as it completely changes one’s environment, he/she has to wear some sort of Virtual Reality equipment, for instance Oculus Rift, HTC Vive or DJI Goggles White etc which levitates the user from their natural environment and put them into the Virtual World. On the Contrary, Augmented Reality only requires a transparent screen in between the object and the user’s eyes in order to render the superimposed objects on top of the natural environment.
The role of AI in implementing Augmented Reality comes in handy when an object itself identifies its rotation, position and orientation with respect to the Real World object and automatically maps itself onto the Real World coordinates such that it always lays on top of the object making a sensible and meaningful representation. Even if the position of the object is later on moved or is rotated by an angle, the augmented visuals remain on the same position with the same orientations as initially designed. the below video sampling a few Augmented Reality examples give a vivid picture of the complete scenario:
The results obtained as in above video uses some methodologies of Augmented Reality Types to achieve the final representation. These types are classified into several forms described below:
Augmented Reality Types:
Marker Based Augmented Reality:
In a Marker Based Augmented Reality, the user holds a camera to an object and the camera identifies a predefined marker, such as a QR code. If it finds a specific QR code containing the information required, it renders the Augmented reality graphics onto the screen for the user to see. The use of QR code in this type of AR is to ease the recognition of objects as a QR code is easily recognized by the camera and no additional image processing is required to gather information. Secondly, the QR code can contain more information as to the position or orientation of image to be rendered and that too, is easily readable form it.
Markerless Augmented Reality:
This type of AR makes use of a device embedded GPS, digital compass, velocity meter, or an accelerometer to identify and mark any familiar object in a near by vicinity onto the screen. it is the most widely used AR type finding its basic application in locating map directions, nearby eateries, businesses, hotels etc.
The role of AI over here is to find nearby landmarks and buildings using devices’ gps and then locating them on the camera. hence, AI plays a major role in this technique to ease human lives.
Projection Based Augmented Reality:
In projection based AR, an artificial light is used which is projected onto a physical object of interest. The light itself contains different segments of various spectrum, each constituting to an action to be performed on the object by the user. Once the user interacts with the light, a corresponding trigger fires, sent over to AR light spectrum and the resulting action performed accordingly. An application of this technology is found in Laser plasma to project a three – dimensional interactive hologram into mid air.
AI here comes in handy detecting the change in color spectrum when the light is interrupted by a human hand.
Superimposition Based Augmented Reality
Superimposition based AR, as the name suggests superimposes an object onto a screen such that the object was actually present, giving the user an enhanced and visualized image. This is essential in helping humans to make judgements or calculations based on what they gather from their naked eye.AI here is responsible for image recognition and identification of objects in the picture in order to superimpose any new objects onto the correct location in accordance to its surroundings, so that the final picture should convey a meaningful message and avoid overlapping or inappropriate rendering of objects. Hence, AI here plays an important role in modifying human perceptions.
Augmented Reality Implementation devices:
Sensors and Cameras
They tend to be the input devices for Augmented reality. They gather data in the form of pictures, videos, device orientation and feed them to the augmented reality soft wares to get processed.
A real world environment data attained in real time via some sort of sensory input device, for instance a camera or a microphone and then an augmented data may be added on top of it.[3]
Projection
The projector is basically the equipment which turns the augmented object into various different orientations to give a better understanding of the whole picture. However, it keeps into consideration that even while turning and rotating the object, the overall picture should map accordingly onto the surface of the image.In this scenario, AI comes into effect which judges and decides whether the object is in acceptable orientation to the background image at all times or not.
With the rapid growth in information and communication technology, the electronic devices enabling extensive AI features and Augmented reality tend to go more cheaper and smaller, hence enabling the creation of more intelligent equipment gradually. Therefore, with fast intelligent systems emerging, the technology would soon fade off “as it will be more readily available embedded into physical objects”[4].
Processing
The devices used in processing and generating Augmented reality features require a significant amount of processing power. They may be regarded as mini computers well trained, cut and designed for the very specific purpose they are meant for. Therefore, “they include a CPU, a GPU, some sort of memory devices for instance, a flash memory, a RAM, some correspondence devices i.e a Bluetooth/Wifi microchip, a GPS and even more”[5].
There is also a possibility that some advanced devices, for instance Microsoft Hololens may also have embedded accelerometer, a gyroscope, and a magnetometer. These devices use AI features to intelligently collect data relating to the speed and the tilt of our head. Further, they can also acquire from our head movement of exactly where our location is with respect to the north, south of the Earth.
Reflection
Augmented Reality Applications:
In surgical – hospitals:
the above video mentions the basic advantages Augmented Reality gave to surgeries in operating rooms:
- Camera Augmented Mobile C-arm
- Freehand SPECT
- Mirracle: Augmented Reality Magic Mirror
In Logistics:
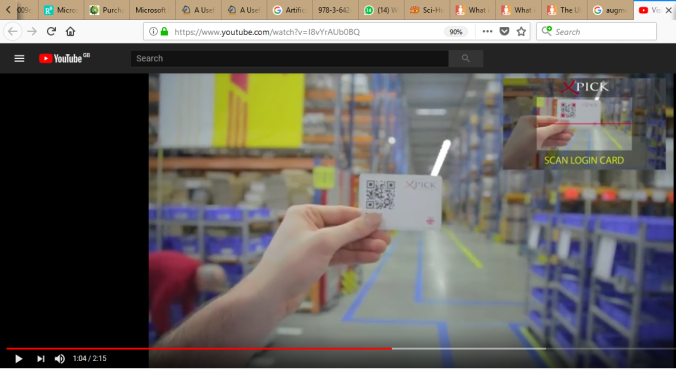
Vision picking in Logistics provide smooth business flow and fast delivery outcomes.
In Advertising:
Ikea: An app that uses Augmented Reality to place IKEA furniture in user’s homes.
Again, in all above examples, AI is used to identify the correct placement of Augmented reality objects. For instance, an IKEA sofa should be on a position that user perceives it to be placed on the ground and not alleviated from it is achieved by the principles of AI.
With such highly renowned companies moving towards Augmented Reality and with its evident and effective use in almost every field of life will surely make Augmented Reality an essential part of future
References:
[1]. [Yu D., Jin J.S., Luo S., Lai W. Huang Q. 2009]













